The Essential eCommerce SEO Audit Checklist: Get More Traffic and Sales

Getting your eCommerce store to rank in organic search results can seem daunting. With so many tasks to tackle, from keyword research to technical optimisation, the complexity of SEO for eCommerce can feel overwhelming.
However, this is where an eCommerce SEO audit checklist is your best friend. Think of it as your roadmap. It breaks down the mammoth task into manageable, actionable steps, ensuring you don’t miss any crucial elements that could boost your store’s visibility online.
Whether it’s ensuring your images are optimised for faster loading times or fixing your eCommerce website structure so that search engines can crawl it efficiently, a checklist systematically guides you through these steps.
This systematic approach takes the guesswork out of SEO, turning what seems like a mammoth task into a series of achievable goals.
As an eCommerce agency, we’ve completed many SEO audits for eCommerce clients over the years. That’s why we’ve created an eCommerce SEO audit checklist, so you don’t have to. This means you can skip the steep learning curve and dive straight into optimising your site, leveraging our expertise to spot and fix issues faster.
On-page SEO is all about making your web pages more search-engine friendly. Unlike off-page SEO, which involves external signals like backlinks, on-page SEO deals with the aspects of your website that you have direct control over, such as content, structure, and HTML elements. This is super important for eCommerce because it helps search engines understand your site better and makes shopping smoother for your customers.
In this checklist, we will cover four key areas:
- On-page SEO: This includes optimising elements on your website like meta tags, headers, images, and internal links to improve your site’s visibility and relevance to search engines.
- Off-page SEO: This focuses on external factors such as backlinks and social signals that influence your site’s authority and ranking in search results.
- Technical SEO: This area ensures that your website meets the technical requirements of search engines, including site speed, mobile-friendliness, and secure connections.
- Content strategy: This involves creating and managing high-quality, relevant content that attracts and engages your target audience, while also improving your site’s SEO performance.
This checklist will guide you through the simple steps you need to boost your website’s visibility in search engines, attract more visitors, and increase sales. You’ll discover practical tips on how to pick the perfect keywords, craft content that search engines love, build valuable links, and handle the techy bits of SEO to make your website perform better.
A foreword on SEO tools
Before diving into our SEO audit checklist, it’s worth highlighting the value of SEO tools. Industry favourites like Semrush, Ahrefs, and Moz are indeed powerful and can save you huge amounts of time. However, they come with a hefty price tag. If your budget is tight, take advantage of their free trials to get a feel for what they offer.
For more budget-friendly options, consider Mangools or SE Ranking. Both offer excellent value and robust features without breaking the bank. To get started, it’s a good idea to assess your store’s SEO performance using this free eCommerce SEO audit.
While this article frequently references Semrush (our SEO tool of choice at Rixxo), we’ve also included free yet effective methods, such as leveraging Google for keyword research. These methods might be slower but can still yield valuable insights for your SEO strategy.
Ready to get started? Let’s jump right in.
Section 1: On page SEO
On-page SEO is all about making your web pages more search-engine friendly. Unlike off-page SEO, which involves external signals like backlinks, on-page SEO deals with the aspects of your website that you have direct control over, such as content, structure, and HTML elements. This is super important for eCommerce because it helps search engines understand your site better and makes shopping smoother for your customers.
To measure the effectiveness of on-page SEO, various metrics are used by tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Moz. For instance, SEMrush provides a ‘Site Health’ score, which evaluates the overall technical health of your website. It includes factors such as crawlability, security, and page speed. Additionally, SEMrush uses ‘On-Page SEO Checker’ to provide suggestions for improvement based on current SEO best practices.
Other important metrics include:
- Content Score: This measures the quality and relevance of your content in relation to targeted keywords. Tools like Clearscope and MarketMuse analyse your content and provide a score based on how well it matches the search intent and keyword usage.
- Keyword Density: This metric assesses the frequency of targeted keywords within your content. While overuse (keyword stuffing) is penalised, a well-balanced keyword density helps search engines understand the main topics of your page.
- Meta Tags Analysis: This involves evaluating the effectiveness of your meta titles and descriptions. Tools like Ahrefs and Moz can help analyse the length, keyword usage, and overall relevance of these elements.
- Internal Linking: The structure and quantity of internal links are vital for on-page SEO. Metrics here include the number of internal links pointing to a page and the anchor text used. This helps distribute page authority and enhances user navigation.
- Page Load Speed: Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and GTmetrix measure how quickly your web pages load. Faster-loading pages provide a better user experience and are favoured by search engines.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Given the increasing number of mobile users, it’s crucial to ensure your site is mobile-friendly. Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test and other tools provide insights into how well your website performs on mobile devices.
Keyword research
Keyword research is fundamental to any SEO strategy. It involves identifying the terms your potential customers use when searching for products like yours online. To bring this to life, let’s consider how one might search for “sweaters”.
How to use Google’s autocomplete function
When you start typing “sweaters” into the Google search bar, you’ll notice a list of autocomplete suggestions. These are popular queries that include your initial term. You might see suggestions like “sweaters for women”, “sweaters on sale”, or “sweaters for winter”. This feature is a goldmine for uncovering long-tail keywords and understanding what your audience is looking for. Simply type in your product and note down the suggestions that resonate with your inventory and marketing goals.
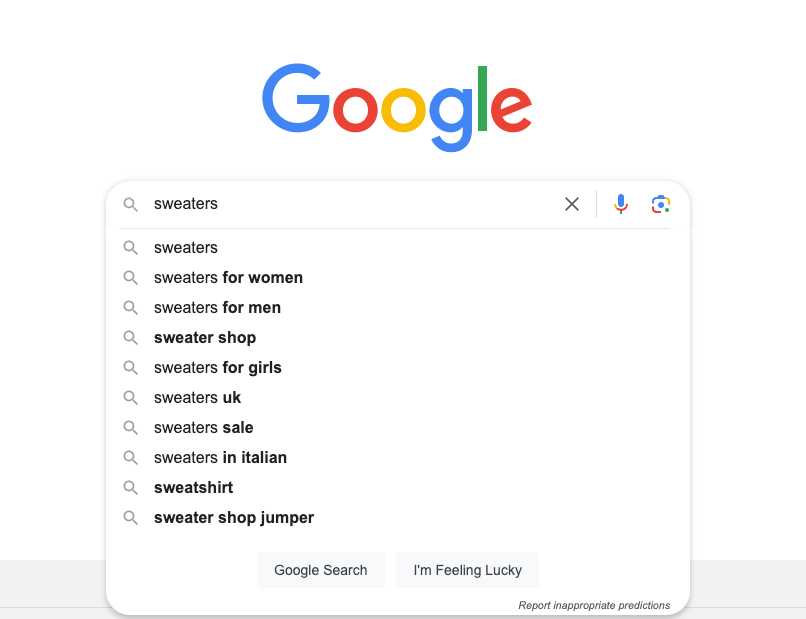

When you start typing “sweaters” into the Google search bar, you’ll notice a list of autocomplete suggestions. These are popular queries that include your initial term.
You might see suggestions like “sweaters for women”, “sweaters on sale”, or “sweaters for winter”. This feature is a goldmine for uncovering long-tail keywords and understanding what your audience is looking for. Simply type in your product and note down the suggestions that resonate with your inventory and marketing goals.
Utilising Semrush’s Keyword Magic tool
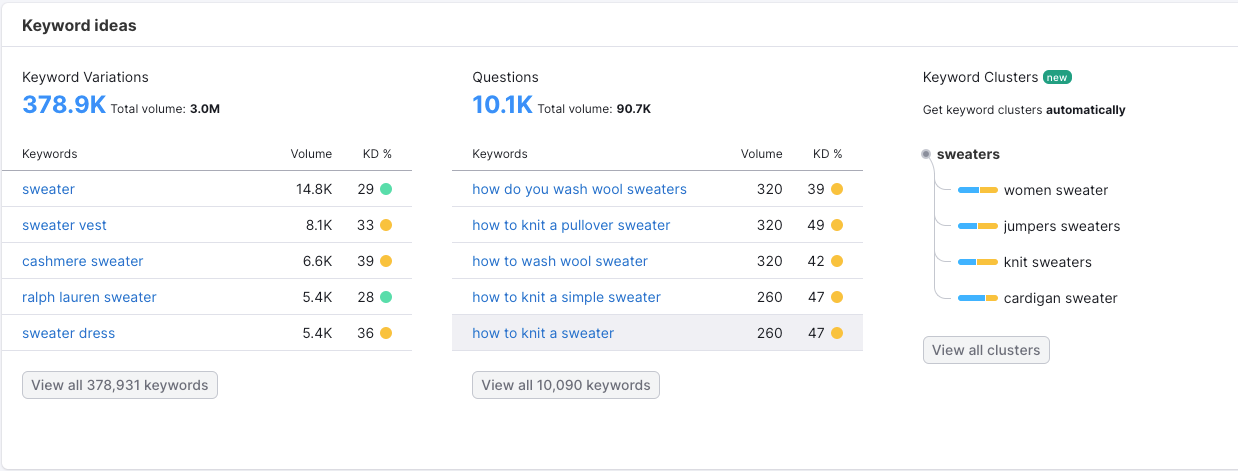
To delve deeper, tools like the Semrush Keyword Magic Tool can expand your list of potential keywords. Enter “sweaters” into the tool, and it will provide a comprehensive list of related search terms, complete with valuable data on search volume, keyword difficulty, and competitive density. This tool is invaluable for identifying seed keywords that can form the basis of your content and SEO strategy.

Understanding search intent
Search intent is the reason behind a search query, and it’s often ignored.
It’s important to match your content with what people are looking for when they use specific keywords. For example, if someone searches for “buy cashmere sweaters online,” they are likely ready to make a purchase. On the other hand, if they search for “best sweaters for cold weather,” they are probably just researching.
In these two examples, you should optimise a product page for the keyword “buy cashmere sweaters,” while the keyword “best sweaters” would be perfect for a blog post.
By understanding and matching search intent, you can create content that meets your audience’s needs at different stages of their buying journey.
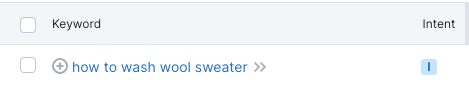

Semrush makes the identification of search intent much easier. For every keyword, there is an “Intent” column.
There you will see one, or two, of the following intents:
- Navigational: Users are looking for a specific page
- Informational: Users want to learn about something (e.g., “how to wash a wool sweater”)
- Commercial: Users want to research before making a purchase decision (e.g., “best cashmere sweater”)
- Transactional: Users want to complete a specific action such as purchase (e.g., “buy wool sweater”)
Selecting a mix of keywords for targeting
Your keyword strategy should include a balanced mix of short-tail, medium-tail, and long-tail keywords. Short-tail keywords, like “sweaters”, are broad and highly competitive but can attract significant search volumes. Medium-tail keywords, such as “men’s wool sweaters”, balance search volume and specificity.
Long-tail keywords, like “women’s cable knit sweaters for winter”, target specific queries and are less competitive, but can often result in higher conversion rates. By targeting a mix, you can capture traffic across the spectrum of search intent and competition levels, optimising your visibility and reach.
Incorporating a thoughtful mix of these keyword types into your SEO strategy ensures you’re not only visible across a wide range of search queries but also highly relevant to your target audience’s needs and moments of intent.
<h1>Women's cashmere sweater</h1>H1 tags play a pivotal role in search engine optimisation (SEO) as they are often the first element search engines and users encounter on a webpage. Acting as the digital equivalent of a newspaper headline, they provide a clear indication of the content’s subject matter. For search engines, H1 tags help determine the relevancy of the content to search queries, thereby influencing the page’s ranking. For users, they offer an immediate understanding of what to expect from the content, enhancing user experience.
Targeting the main keyword in the H1
Incorporating your main keyword into the H1 tag is important. This signals to search engines the primary focus of your content, aiding in better alignment with search queries. For instance, if your page is dedicated to promoting “best cashmere jumpers”, an effective H1 tag could be “Discover the Best Cashmere Jumpers for 2024”. This targets the main keyword but also makes the heading intriguing and informative for potential readers.
Ensuring uniqueness and optimisation
Each web page must feature a unique, keyword-optimised H1 tag. This uniqueness aids search engines in differentiating between pages, ensuring they serve the most relevant content to users based on their search queries. The practice of optimising each H1 tag with specific keywords relevant to the page’s content boosts your website’s SEO performance.
Adhering to best practices
Limiting H1 tags to one per page is a widely recommended best practice. This simplification helps search engines and users alike to identify the primary focus of the page, without confusion. Keeping H1 tags within the 50-60 character range ensures they are concise enough to be fully displayed in search results, avoiding truncation and ensuring the message is clearly communicated.
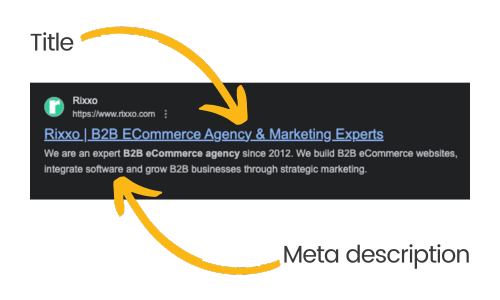
<title>Rixxo | B2B eCommerce Agency & Marketing Experts</title>Title tags serve as the name of a web page and play a role in both SEO and user experience. While they share similarities with H1 tags, such as including main keywords, they serve different purposes and appear in different contexts.
A title tag is an HTML element that specifies the title of a web page. This title appears in the browser tab and, more importantly, as the clickable headline in search engine results pages (SERPs).


Unlike H1 tags, which are displayed prominently within the content of the page and guide the reader through the content, title tags are primarily designed to catch the attention of users and search engines in the SERPs.
It’s beneficial to align your title tags with your H1 tags to maintain consistency and relevancy. However, adjustments may be necessary to incorporate branding or to adhere to optimal lengths. For example, while your H1 might be “Discover the Best Cashmere Jumpers for 2024”, your title tag could be slightly modified to include branding or to be more concise, like “Best Cashmere Jumpers 2024 | YourBrandName”. This ensures that your page is recognisable in SERPs and provides clear expectations about the content.
Positioning of target keywords
Including target keywords towards the beginning of your title tag is a best practice that can improve your page’s relevancy and visibility in search results. Search engines attribute more weight to keywords that appear early in the title tag, making it more likely that your page will rank well for those terms. For users, it immediately communicates that your content is relevant to their search query.
Adhering to character limits
Keeping title tags within the 50-60 character range is essential for ensuring that they are fully visible in SERPs without being cut off. This limit helps to succinctly convey the content’s value proposition and encourages clicks without overwhelming users with too much information. A well-crafted title tag that fits within this range can effectively grab attention and draw visitors to your website.
By understanding and applying these principles to your title tags, you can significantly enhance the visibility and attractiveness of your pages in search results, driving more targeted traffic to your site.
Meta descriptions
<meta name="description" content="We are an expert B2B eCommerce agency since 2012. We build B2B eCommerce websites, integrate software, and grow B2B businesses through strategic marketing.">A meta description is a brief summary that appears under your page’s title in search engine results. Its main purpose is to give searchers a snapshot of what to expect from the page, encouraging them to click through.

A well-crafted meta description can significantly impact click-through rates (CTR). Offering a concise preview of the page’s content, it helps users decide whether the page contains the information they’re seeking, acting as a “pitch” to entice potential visitors to click through to your site. This increased engagement signals to search engines that your page is valuable and relevant to search queries, which can indirectly improve your rankings.
Crafting unique meta-descriptions
For maximum benefit, it’s helpful to write unique meta descriptions for each page on your website, integrating target keywords to highlight the relevance of your content to search queries. This not only aids in attracting the right audience but also improves the user’s search experience by providing clear and accurate representations of your web pages.
Adhering to character limits
Keeping your meta descriptions under 160 characters ensures they fit within the display limits of most search engines, preventing them from being cut off mid-sentence. A concise meta description delivers the essential message of the web page quickly and effectively, encouraging more clicks.
Leveraging AI for meta descriptions
Here’s a simple tip to simplify writing meta descriptions: use AI writing tools. These tools help create short, catchy summaries that match your content and keywords. Just give a few details about your page and the keywords you want to target, and the AI will do the rest. This can save you a lot of time, especially if your website has many pages. It also helps keep your meta descriptions consistent and high-quality.
Your meta descriptions can make your website pop in search results. This means more people might click on your site, potentially bringing in more visitors.
Page URLs
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the address of a webpage, allowing users and search engines to locate and access content online. Beyond their functional role, URLs play a part in a website’s SEO and user experience. Well-optimised URLs can contribute to a page’s visibility and ranking in search engine results.
Optimising URLs with target keywords
Including target keywords in your URLs reinforces the relevance of your content to search engines while enhancing user understanding of what to expect from your page. For instance, a URL of:
www.yourbrand.co.uk/best-cashmere-jumpers
is immediately clear and informative, both to search engines and potential visitors. It’s a good practice to ensure your URLs accurately describe the page content, while including target keywords.
Using hyphens and removing unnecessary parameters
Hyphens are the preferred method for separating words in URLs, making them more readable for both users and search engines. Unlike underscores or spaces, search engines universally recognise hyphens as word separators. Additionally, it’s important to avoid unnecessary parameters, such as session IDs, which can clutter your URLs and detract from their readability and SEO value.
For example, instead of www.yourbrand.co.uk/products?item=123, a cleaner URL would be www.yourbrand.co.uk/cashmere-jumpers.
Keeping URLs concise
While it’s beneficial to include keywords and descriptive terms in your URLs, brevity remains key. Overly long URLs can be daunting for users and may detract from the overall user experience. They can also be cut off in search results, losing valuable context. Aim for a URL length that balances descriptiveness with conciseness, ensuring it remains impactful and easy to understand at a glance.
By adhering to these considerations—targeting keywords, using hyphens for separation, removing unnecessary parameters, and keeping URLs concise—you can enhance the effectiveness of your URLs in SEO. Well-crafted URLs contribute to better ranking, user experience, and ultimately, the success of your website.
Breadcrumbs help users understand and navigate a website’s hierarchy without having to rely on the back button or the site’s main navigation menu. Named after the trail of breadcrumbs left by Hansel and Gretel in the classic fairy tale, breadcrumb navigation provides a path for users to follow back to the starting or entry point of a website and shows where the current page is located in the site’s structure.
Importance to eCommerce
Breadcrumb navigation is essential for eCommerce sites. It lets customers smoothly move between categories and products, improving their shopping experience. This can lead to more product exploration and potential sales. Breadcrumbs also lower bounce rates by making it easier for users to keep shopping or check out related categories if they don’t immediately find what they need.
Enhancing UX and SEO
Breadcrumb navigation enhances user experience (UX) by simplifying navigation and making the website more user-friendly. From an SEO perspective, breadcrumbs can contribute to better site indexing by search engines, as they offer an additional layer of navigation that search engine crawlers can follow. Furthermore, Google sometimes includes breadcrumbs in search results, making your listing more attractive and improving click-through rates.
- Magento: Magento offers built-in support for breadcrumb navigation, which can be enabled and customised through the platform’s backend. Navigate to the theme settings under the ‘Content’ section, where you can find options to enable or modify the breadcrumb trail according to your site’s hierarchy and design preferences.
- WordPress: For WordPress users, breadcrumb navigation can be easily added using plugins or theme features. One of the more popular plugins for this purpose is Rankmath, which offers an easy-to-use breadcrumb setup.
Adding breadcrumb navigation to your eCommerce site, no matter the platform, boosts UX and SEO. Breadcrumbs make navigating your site clearer and easier, improving the shopping experience and fostering customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Image SEO
Image SEO helps boost the online presence and user experience of eCommerce sites. Since most online shoppers base their buying decisions on product images, optimising these images can enhance your site’s search engine ranking and customer satisfaction.
Using descriptive file names with relevant keywords
Start by ensuring your image files have descriptive names that reflect the image content, including relevant keywords where possible. This practice helps search engines understand and index your images more accurately.
For example, instead of naming a file “IMG_123.jpg”, a more descriptive name would be “blue-cotton-summer-dress.jpg”. This not only helps search engines but also improves the likelihood of your images appearing in related image searches, driving additional traffic to your site.
Introduction to the alt tag
<img src="image.jpg" alt="Description of the image">The alt tag, short for “alternative text”, serves two main purposes.
First, it provides a text alternative for images on web pages, aiding users who are visually impaired and rely on screen readers to browse the internet. This makes your website more accessible and inclusive, aligning with Google’s best practices for accessible web design.
Second, alt tags offer search engines context about the content of your images, which can enhance your site’s SEO if the tags include relevant keywords.
Adding concise alt text
When adding alt text to your images, aim for concise descriptions that accurately reflect the image content. Incorporating keywords into your alt text should be done judiciously and only when they genuinely relate to the image.
Remember, the primary goal of alt text is to provide clarity and context, not to stuff keywords.
For images that are purely decorative and don’t add informational value to the content, it’s acceptable to leave the alt attribute empty to avoid distracting screen reader users with irrelevant details.
Choosing the right image format and optimising for web use
Selecting the appropriate image format is another key element of image SEO. JPEG is typically preferred for photographs and images with a broad range of colours, while PNG is better suited for images requiring transparency or with less colour variation.
Additionally, always optimise your images for the web by compressing them to reduce file size without significantly compromising quality. This ensures your pages load quickly, enhancing user experience and SEO.
By focusing on these aspects of image SEO, eCommerce sites can significantly improve their online presence, making their products more visible and attractive to both search engines and shoppers.
Internal linking
Internal linking refers to the practice of linking one page of a website to another page within the same website. This technique is a crucial component of on-page SEO, as it not only aids in website navigation but also enhances the information hierarchy for search engines and improves page authority across the site.
Internal linking means connecting one page of your website to another page. It’s a key part of making your site more search engine friendly. Not only does it make your website easier to navigate, but it also helps search engines understand your site’s structure better and boosts page authority across your site.
How internal linking helps SEO
Internal linking supports SEO in several key ways. Firstly, it helps search engines discover new pages through existing links, making indexing more efficient. Secondly, by distributing page authority or ‘link equity’ throughout the site, internal links can help improve the ranking potential of individual pages. Lastly, internal linking significantly enhances the user experience, providing pathways for users to further explore your site, which can lead to increased engagement and lower bounce rates.
Strategies for identifying and implementing links
A strategic approach to internal linking involves careful consideration of how individual pages are related and how they can provide value to the user’s journey. A good use of an internal link would be linking from a blog post about “The Best Fabrics for Winter” to a product category page for “Winter Coats.” This link is relevant, provides additional value to the reader, and encourages exploration of your product range.
Conversely, a bad use of an internal link would be linking from a blog post about “Summer Beachwear Trends” to a product page for “Winter Coats” without any contextual relevance or explanation. This could confuse users and detract from the user experience, potentially increasing bounce rates.
Using descriptive links
The anchor text, or the clickable text portion of a link, should always be descriptive and relevant to the target page. Using non-descriptive words like “click here” or “this page” for a link is a missed opportunity for reinforcing relevancy and providing context to both users and search engines. Descriptive links should clearly indicate what the user can expect to find when they follow the link. For example, instead of “Click here for more,” use “Explore our collection of winter coats” as the anchor text.
<a href="https://www.example.com/winter-coats">Explore our collection of winter coats</a>This method boosts SEO and enhances accessibility for users who rely on screen readers, as it provides clear information about the link’s destination.
By implementing thoughtful internal linking strategies and ensuring links are descriptive and contextually relevant, websites can significantly improve their SEO performance, user engagement, and overall site authority.
Section 2: Off-page SEO
Off-page SEO is all about what you do outside your website to help you rank higher in search results.
It’s different from on-page SEO, which is about making changes on your website. Off-page SEO means making connections and showing off how relevant, trustworthy, and authoritative your website is through other means. This could involve getting links from other respected sites, using social media marketing, or working with influencers.
For eCommerce, an off page strategy helps you become more visible and trusted on the internet. If you do off-page SEO right, you can move up in search rankings, attract visitors from various sources, and potentially increase your sales.
Getting links from reputable sites, staying active on social media, and making smart partnerships can really help spread the word about your brand and boost your overall SEO efforts, complementing the work you do on your site.
Acquire high-quality backlinks
Backlinks, also known as inbound links or external links, are links from one website to a page on another website. They are helpful because they signal to search engines that others vouch for your content. If many sites link to the same webpage or website, search engines can infer that content is worth linking to, and therefore worth surfacing on a SERP.
Consequently, earning these backlinks can boost a site’s ranking position or search visibility.
Creating linkable content
One of the most natural and sustainable strategies to acquire backlinks is creating linkable content. This refers to content that is so valuable, informative, or entertaining that other websites want to share it with their readers. Examples include original research, comprehensive guides, infographics, or compelling stories. Content that naturally acquires links does so because it adds value to the linking site’s audience, rather than because the link was sought out or paid for.
Using tools to identify backlink opportunities
Tools like Semrush’s Link Building Tool can streamline the process of identifying opportunities for backlinks from high-authority sites. By entering your website’s details, you can discover which websites are worth approaching for backlinks based on their relevance and authority. This approach allows you to target your efforts more effectively, focusing on backlinks that will make a real difference to your SEO.
Toxic Backlinks
Not all backlinks are good for your website’s SEO. Toxic backlinks come from low-quality or spammy websites and can hurt your site’s ranking. Search engines, especially Google, may penalise your site if it has links from these bad sources.
Spam backlinks can build up over time, and it’s hard to prevent them completely. However, you can manage them with the right tools.
For example, Semrush can help you find toxic backlinks. Once identified, you can use the disavow tool in Google Search Console to tell Google to ignore these links. This helps protect your site from any negative effects caused by toxic backlinks.
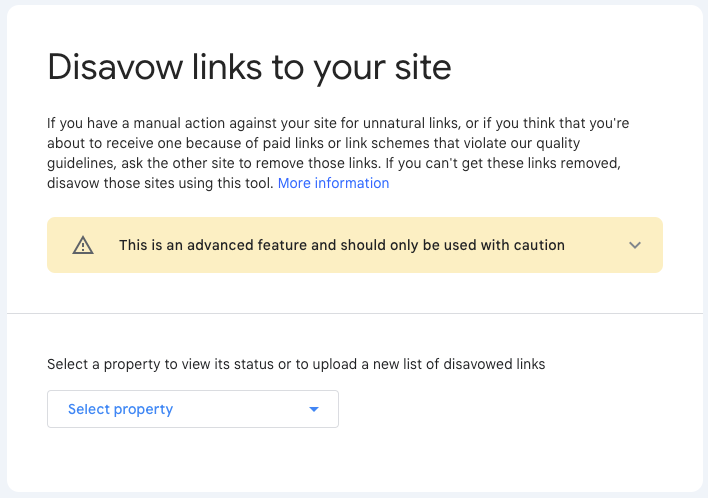

In short, getting good backlinks is key to any SEO plan because it helps your website show up better in search results. By making content that others want to link to and using tools to keep track of your backlinks, you can make sure these links are helping, not hurting, your SEO work.
List your website in business directories
For eCommerce stores, getting your business listed in well-known directories can be a smart way to get noticed, earn trust, and bring more visitors to your website. Being on sites like Google Business Profile, Better Business Bureau, and Yelp helps people find your business and gives you helpful backlinks that can boost your search engine ranking.
Directories play a role in local SEO by helping businesses show up in local search results and on maps, which is particularly beneficial for eCommerce businesses with physical stores or those targeting specific geographic areas. Even purely online businesses can benefit by appearing more trustworthy and established.
Google Business profile
The Google Business Profile (formerly Google My Business) is powerful for increasing visibility across Google services, including Search and Maps. Here are some tips for optimising your profile:
- Complete every section: Google favours completed profiles. Fill in every section with accurate, up-to-date information to maximise your profile’s effectiveness. This includes your business name, address (if applicable), phone number, website URL, and hours of operation.
- Use high-quality photos: Images boost user engagement. Upload high-quality photos of your products, storefront (if applicable), and any other images that accurately represent your business.
- Collect and respond to reviews: Customer reviews improve your business’s visibility and appeal. Encourage satisfied customers to leave positive reviews and respond thoughtfully to all reviews, showing that you value customer feedback.
- Post updates regularly: Google Business Profile allows you to post updates, special offers, events, and more. Regular posts keep your profile active and engaging for potential customers.
- Select appropriate categories: Choose categories that accurately describe your business to improve its visibility for relevant searches. Be as specific as possible.
By using business directories, like your Google Business Profile, online stores can boost visibility and draw in more customers. It’s important to make sure your business information is the same and correct across all directories. This helps make your business look more reliable and can also help your search engine rankings.
Social media platforms can indirectly boost your SEO by increasing brand visibility and driving website traffic.
Importance for eCommerce SEO
Social media doesn’t directly affect SEO rankings but enhances online visibility. Profiles often appear in search results, and shared content can lead to more website traffic and backlinks.
Profile optimisation tips
- Complete your profiles: Include your website, contact info, and a business description.
- Use high-quality visuals: Ensure your profile and cover photos are clear and branded.
- Incorporate keywords: Help users find your brand by using relevant keywords.
- Stay active: Post regularly and engage with your audience to increase visibility.
Optimising your social media profiles improves your eCommerce brand’s reach, contributing to a solid SEO foundation.
Build strategic partnerships
Working with influencers, bloggers, and experts is a great move for online businesses wanting to get more links and visibility. Teaming up can spread the word about your brand, bring more visitors to your site, and help your search engine ranking by getting quality links back to your website.
When you partner with respected people or companies in your field, they might naturally mention and link to your site in their content. This not only brings in visitors directly but also makes search engines see your site as more credible, which can help you rank higher. Plus, the trust and buzz from these partnerships can make more people notice and trust your brand.
Leveraging partnerships for SEO benefits
To maximise the SEO benefits of strategic partnerships, consider the following approaches:
- Collaborate on content: Work with influencers or industry bloggers to create mutually beneficial content. This could include guest blogging, interviews, or co-created guides.
- Product reviews: Send your products to influencers for honest reviews. If they’re posted online with a link back to your site, it can lead to increased visibility and traffic.
- Host events or webinars: Collaborate on events or webinars, encouraging partners to link back to your registration page.
By strategically engaging with influencers and industry professionals, eCommerce businesses can enhance their SEO, gain valuable backlinks, and increase their online presence.
Section 3: Technical SEO
Technical SEO is about making sure the technical parts of your website are set up right so search engines can easily find and understand your site. It involves a lot of behind-the-scenes work like organising your website’s structure, making URLs easy to follow, speeding up your site, making sure it works well on phones, adding security features, and setting up sitemaps. This kind of SEO helps your website show up better in search results.
For eCommerce, technical SEO is super important because these websites have lots of pages and products, and things change a lot. A good technical setup helps search engines quickly find and list all your products, which means more people can find what you’re selling through a search.
Also, technical SEO makes your website nicer for people to use. Fast loading times, being easy to use on a phone, and having a secure site are all important for keeping visitors happy and more likely to buy something. So, focusing on technical SEO can help online shops be more successful on search engines, bring in the right kind of visitors, and sell more.
<link rel="alternate" href="http://www.example.com/en-us" hreflang="en-us" /> <link rel="alternate" href="http://www.example.com/en-gb" hreflang="en-gb" />Hreflang tags are a method of telling search engines about the language and geographic targeting of a webpage. These tags help search engines display the correct version of a page to users based on their language preferences or geographic location. For eCommerce sites that cater to a diverse, global audience, implementing hreflang tags is essential to ensure that users are directed to the content most relevant to them.
What is an hreflang tag for?
The hreflang tag is used to specify the language and geographical targeting of a webpage. When a website has multiple versions of the same page in different languages or for different regions, hreflang tags help search engines understand which version of the content is appropriate for users in a specific location or who speak a specific language. This is crucial for providing a user-friendly experience on multilingual eCommerce sites, as it directs users to the content in their preferred language.
Using hreflang tags can impact your SEO and user experience. Without these tags, search engines might display the wrong language or regional version of your site in their results, which can confuse users and lead to a higher bounce rate. Correctly implemented hreflang tags improve the chances of your content ranking well globally, ensuring that users around the world see the appropriate version of your site.
Tips for implementation
- Ensure accuracy: Double-check the language and regional codes you use in your hreflang tags to avoid directing users to the wrong versions of your site.
- Use a sitemap: Implementing hreflang tags in your XML sitemap can be more efficient, especially for large, multilingual sites. This approach makes it easier for search engines to crawl and understand the language and regional targeting of your pages.
- Avoid common mistakes: One common mistake is forgetting to include a self-referencing hreflang tag, which tells search engines that the page is specifically targeted to a particular language or region. Also, ensure there is a complete cycle of tags; every page that uses hreflang tags should reference all other language or regional versions, including itself.
- Consistency is key: Make sure that your hreflang tags match the content actually presented on the page. Inconsistencies between the tag and the page’s content can lead to search engines ignoring your hreflang annotations.
By carefully implementing hreflang tags and avoiding common pitfalls, eCommerce sites can improve their global search visibility and offer a better browsing experience to international customers.
Optimise page loading speed
Page loading speed refers to the amount of time it takes for a webpage to fully display its content to a user. It’s a critical aspect of website performance, directly influencing user experience, conversion rates, and SEO. Page speed is measured in seconds, typically using tools that simulate how long a page takes to load from the moment a user requests it.
Why does page speed matter for SEO?
Google and other search engines prefer websites that load quickly because they make users happy. If a website is slow and takes too long to load, people might give up and leave (this is referred to as a high “bounce rate”), which is bad for both the person visiting the site and the site’s chances of appearing high up in Google’s search results.
How can it be measured?
GTmetrix is a handy tool that checks how quickly your website loads. It tells you what’s making your site slow and advises how to make it faster. You just put your website’s address into GTmetrix, and it gives you a report on how long your page takes to load and tips on how to speed it up.
Another useful tool is Google’s PageSpeed Insights. It analyses your website’s performance on both mobile and desktop devices. PageSpeed Insights provides a detailed report with scores and suggestions to improve your site’s speed, helping you enhance user experience and search engine ranking.
Methods of improving page speed
Several strategies can significantly reduce load times and improve your site’s performance:
- Optimise images: Ensure your images are no larger than necessary, compressed for the web, and in the right file format (JPEG for photos, PNG for graphics with transparent backgrounds).
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML: Removing unnecessary characters from your code (like spaces, comments, and line breaks) can speed up processing times.
- Leverage browser caching: Set up your web server to instruct browsers to store key website resources on local devices, speeding up load times for repeat visitors.
- Use a content delivery network (CDN): CDNs distribute your content across multiple, geographically dispersed servers, reducing the distance between users and website resources.
- Enable compression: Use tools like Gzip to reduce the size of your CSS, HTML, and JavaScript files, which can drastically reduce their transfer time.
- Eliminate render-blocking JavaScript and CSS: If your site’s code halts the browser from rendering the page until specific JavaScript and CSS files are loaded, consider deferring or asynchronously loading these resources.
Improving page loading speed is a continuous process that can enhance user experience and support your SEO efforts. By regularly monitoring your site’s performance and implementing the above strategies, you can ensure your website remains fast, efficient, and competitive in the digital landscape.
Create a robots.txt file
A robots.txt file is a text file placed in the root directory of your website that instructs web crawlers (robots) on how to crawl pages on your website. It’s used to manage and restrict the crawling of specific sections of your site, ensuring that search engines prioritise indexing the most important content.
Here’s an example of what a simple robots.txt file might look like:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /private/
Disallow: /tmp/
Allow: /
Sitemap: <https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml>Here’s a breakdown of what each part means:
User-agent: *: This applies to all web crawlers. The asterisk * is a wildcard that means “all”.
Disallow: /private/: This tells web crawlers not to go into the /private/ directory of the website.
Disallow: /tmp/: This tells web crawlers to stay out of the /tmp/ directory as well.
Allow: /: This line isn’t always necessary but can be used to explicitly allow access to the rest of the site. It says everything else on the site is okay to visit.
Sitemap: <https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml:> This points crawlers to the website’s sitemap, which is a file listing all the pages on the site to help crawlers find everything
What does the robots.txt file do?
The robots.txt file tells search engine robots which pages or sections of your site should not be crawled and indexed. This is particularly useful for blocking access to duplicate content, private areas, or files and folders that don’t contribute to your SEO. However, it’s important to note that the robots.txt file is a guideline for crawlers, and not all robots will follow these instructions.
The proper use of a robots.txt file is good for SEO as it helps search engines efficiently crawl your site. By preventing search engines from indexing irrelevant pages, you can ensure that only high-quality, content-rich pages are indexed and shown in search results. This can improve your site’s overall SEO by focusing search engine attention on the content that truly matters.
Tips for implementation
- Place it in the root directory: The robots.txt file must be located in the root directory of your website to be found by web crawlers.
- Be specific: Specify which user agents (crawlers) the instructions apply to and clearly state which directories or pages are disallowed from crawling.
- Use it wisely: Avoid blocking content or pages that could positively impact your SEO. Misusing the robots.txt file can prevent search engines from indexing valuable content.
- Check for errors: Use tools like the Google Search Console to test your robots.txt file for errors and ensure it’s effectively managing crawler access as intended.
- Update regularly: As your site evolves, regularly review and update your robots.txt file to reflect changes in your site’s structure and content priorities.
Using a robots.txt file helps manage how search engines interact with your site. By guiding crawlers to your most important pages, you can enhance your site’s SEO performance and ensure that your best content stands out in search engine results.
Set up Google Search Console
Google Search Console (GSC) is a free tool offered by Google that helps you monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot your site’s presence in Google Search results.
Unlike Google Analytics or GA4, which provides broad insights into website traffic and user behaviour, Google Search Console focuses specifically on how Google views your site. This includes showing which of your pages are indexed, identifying crawl errors, and understanding how your site appears in search results.
How Google Search Console differs from Analytics/GA4
While Google Analytics/GA4 offers an in-depth look at website traffic, user engagement, and conversion metrics, Google Search Console provides data directly related to a website’s search performance and visibility.
Search Console tells you exactly how Google’s search engine interacts with your site, which keywords bring users to your site, and how effectively your content is ranked. It’s more focused on the technical aspect of SEO and the site’s relationship with Google Search.
How Search Console can help you improve SEO
Google Search Console is invaluable for enhancing your SEO strategy. Here are a few ways it can help:
- Indexing: GSC lets you see which pages on your site have been indexed by Google and identify any issues preventing indexing. You can also submit sitemaps and individual URLs for crawling and indexing, ensuring that your latest content is visible in search results.
- Search Queries: It provides data on which search queries bring users to your site, including information on your site’s ranking for those queries. This can help you understand what your audience is looking for and how well your content meets their needs.
- Mobile Usability: With mobile search becoming increasingly important, GSC offers reports on mobile usability, highlighting issues that might affect your site’s performance on mobile devices.
- Links: You can see who links to your website and which of your pages are most frequently linked. This can inform your content and link-building strategies.
- Security Issues: If Google finds any security issues with your site, such as hacking or malware, it will notify you through the Search Console, allowing you to address problems promptly.
Setting up Google Search Console involves verifying your ownership of the website, which can be done through several methods, including HTML file upload, domain name provider, HTML tag, Google Analytics, or Google Tag Manager. Once set up, integrating GSC insights into your SEO strategy can lead to significant improvements in your site’s search performance and user experience.
Install an SSL Certificate
An SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate is a digital certificate that provides a secure link between a website and a visitor’s browser. Encrypting data transmitted between the two ensures that sensitive information such as login details, personal information, and payment data are transferred securely.
How does an SSL certificate help SEO?
An SSL certificate is a tool that makes a website more secure, but it also helps the website show up better in Google searches.
Google has said that websites that use HTTPS (which is a secure version of the web, turned on by an SSL certificate) might get a little boost and appear higher in search results.
Also, if a website doesn’t have an SSL certificate, web browsers might show a warning that it’s ‘not secure.’ This can make people leave the site quickly, and Google might notice that and not rank the website as highly.
So, having an SSL certificate is important not only to keep your website safe but also to help more people find it through Google.
How to install an SSL certificate
- Purchase or obtain a free SSL certificate: Many web hosting providers offer free SSL certificates as part of their hosting packages. Alternatively, you can purchase one from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) or obtain a free one from Let’s Encrypt, a non-profit CA.
- Activate the SSL certificate: If you’re purchasing from a CA, you’ll typically need to generate a CSR (Certificate Signing Request) from your hosting control panel and submit it to the CA. If your hosting provider includes SSL, they may handle this step for you.
- Install the SSL certificate on your hosting account: Once issued, you’ll receive your SSL certificate via email or in your account with the CA. You then need to install it on your server. The process varies depending on your hosting provider and server type, but most providers offer detailed guides or customer support to help with installation.
- Update your website to use HTTPS: After installing the SSL certificate, ensure your website uses HTTPS by default. This may involve updating settings in your content management system (CMS), implementing 301 redirects in your .htaccess file to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS, and updating any hard-coded HTTP links to HTTPS.
- Verify the installation: Use an online SSL checker tool to verify that your SSL certificate is installed correctly and that your website is accessible via HTTPS.
By securing your site with an SSL certificate, you not only protect your visitors but also enhance your site’s SEO performance, contributing to a safer and more trustworthy web experience.
Optimise site structure
Site structure refers to how your website’s content is organised and interconnected. It’s the backbone of your website, guiding users and search engines through your pages, from the general to the specific. A well-planned structure makes it easier for search engines to crawl and index your site, improving your SEO rankings. For eCommerce sites, this is important because a logical structure helps customers find the products they’re searching for easily, enhancing user experience and potentially boosting sales.
Product categories
When you set up product categories and smaller groups within those categories, it’s key to think about what your customers are looking for. You want to organise your products in a way that makes sense and feels natural to them.
In eCommerce, the best practice for creating a product category is to ensure that the category has a sufficient number of products to justify its existence and provide value to customers. Generally, a category should contain at least 10-20 products. This range ensures that the category is populated enough to be meaningful and useful for navigation, yet not so sparse that it seems unnecessary.
Take an electronics store as an example. It might have big groups like ‘Laptops’, ‘Cameras’, and ‘Smartphones’. Then, under ‘Laptops’, there could be smaller groups such as ‘Gaming’, ‘Business’, and ‘Personal’ to help narrow down the search. This setup helps shoppers find their way around easily and reflects how they think about these products.
Using clear and straightforward names for each group helps shoppers find exactly what they’re after, making their shopping smoother.
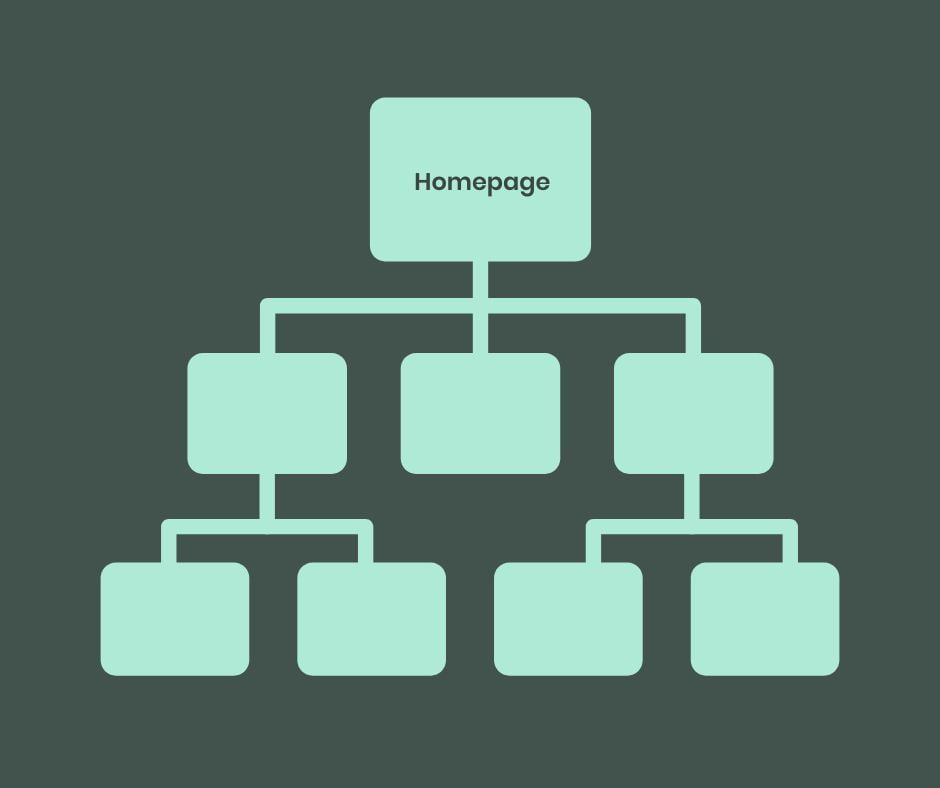

Site hierarchy
Your website structure should look like a pyramid, with the most general page (your home page) at the top, and more specific pages (like product pages) further down. This setup is important for helping people and Google find their way around your site easily.
Keep things simple:
You want your website to have a straightforward structure that’s not too deep. Ideally, someone should be able to get from your home page to any product page by making no more than three clicks, for example:
Home > Category > Subcategory
This makes your website user-friendly for visitors and search engines alike.
Having product pages just a few clicks away from the home page makes for a better experience for your visitors and can also help your website show up higher in Google’s search results. It helps people quickly find what they’re looking for, and it helps Google understand and list your website more effectively.
It’s also smart to make sure your website’s addresses (URLs) show your website’s structure clearly:
www.yoursite.com/category/subcategory/product-name
This keeps things clear for both your visitors and Google.
Make your website mobile-friendly
Smartphones have revolutionised internet access, necessitating responsive design to ensure websites adjust for any device, thus enhancing usability. With mobile devices generating over half of web traffic, having a mobile-friendly site is crucial for eCommerce.
Google prioritises mobile responsiveness in search rankings. Streamlining web forms for mobile enhances usability and SEO, reducing bounce rates and boosting conversions. This signals the site’s value to Google, potentially elevating rankings.
To improve your website’s mobile responsiveness and optimise your forms, consider these practical tips:
- Adopt a mobile-first approach: Design your website with mobile users in mind from the start, ensuring all features work seamlessly on smaller screens.
- Simplify forms: Keep forms short and straightforward, asking only for essential information to make it easier for users to complete them on mobile devices.
- Use large, clickable buttons: Ensure that all buttons and calls to action are easy to click on a touch screen.
- Optimise images and videos: Compress media files to reduce loading times without sacrificing quality, as slow loading times can deter mobile users.
- Test on multiple devices: Regularly test your website’s mobile responsiveness on various devices and browsers to ensure all visitors have a good experience.
By focusing on responsive design and optimised forms, you cater to the growing number of mobile users and improve your site’s SEO, making your eCommerce site more visible and accessible to a wider audience.
Section 4: Content strategy
A content strategy is a plan for making, sharing, and looking after content to draw in and keep the attention of the people you want to reach. It’s important because it helps your brand stand out by giving your audience useful and relevant information.
Your content is how you talk to your audience. A smart strategy means you offer content that really matters to your customers, answers their questions, and meets their needs, instead of just adding more noise.
Search engines prefer high-quality content that fits what people are looking for. By focusing on the right words and creating interesting content, you can make your website more visible and appealing to both people and search engines. This improves your website’s ranking and brings in more visitors.
Write human-firstcontent
Human-first content is clear, relevant, and aligned with what your audience is searching for. It’s about writing in a way that feels natural and engaging to your readers, addressing their questions, needs, and interests directly.
Why does this matter? Because it’s humans who read your content, decide its value, and choose whether to act on it. Search engines are designed to reward content that serves users well. Content that matches user search intent and answers their queries thoroughly tends to rank higher, driving more traffic to your site.
Examples of good vs. poor practice in eCommerce
Good Practice:
- Product descriptions that tell a story: Imagine an online clothing store. A good product description does more than list fabric types; it tells you how the clothing piece fits into your life, like “Our lightweight, breathable summer dress will keep you cool and stylish during those hot summer days.”
- Blog posts that solve problems: A blog post titled “How to Choose the Perfect Running Shoes for Your Feet” offers value by addressing a common question, helping readers make informed decisions, and subtly pointing them towards products in your range.
Poor Practice:
- Overuse of keywords: Stuffing product descriptions or articles with keywords, like “Buy cheap running shoes online, best running shoes, affordable running shoes,” makes the content hard to read and can harm your SEO.
- Irrelevant content: Publishing a blog post on an electronics eCommerce site titled “10 Best Summer Salads” may attract brief attention but doesn’t serve the site’s target audience or business goals.
Writing human-friendly content means focusing on your audience’s needs and interests, crafting your message in a way that’s both informative and engaging. This approach improves your SEO but also builds trust and authority with your readers, encouraging loyalty and repeat visits.
Avoid duplicate content
Duplicate content refers to substantial blocks of content within or across domains that either completely match or are appreciably similar. It’s an issue for SEO because search engines aim to provide the best search experience by displaying diverse sources of information. When multiple pages have the same content, it’s hard for search engines to decide which version is more relevant to a search query. This can lead to a dilution of ranking power among duplicated pages, potentially decreasing the visibility of each in search results.
The challenge for eCommerce sites
eCommerce sites face unique challenges regarding duplicate content. With product descriptions, technical specifications, and manufacturer copy often repeated across multiple products and categories, it’s easy to inadvertently create duplicate content. Moreover, similar products or variants (such as colour or size) can exacerbate this issue, making it difficult for search engines to distinguish between them.
Identifying duplicate content
Here are three strategies or tools commonly used:
- Google Search Console: This tool helps identify issues that Google has detected on your website, including duplicate content. By using the Coverage report, you can see if Google has flagged any of your pages as duplicates.
- Copyscape: This online plagiarism checker allows you to enter a URL to find out if there are any other pages on the internet with the same content. It’s useful for checking if product descriptions on your site appear elsewhere on the web.
- Sitebulb website audit tool: This desktop program crawls websites’ URLs and analyses them for SEO issues. It can help identify duplicate page titles, descriptions, and even body content, giving you a comprehensive view of content duplication on your site.
Addressing duplicate content involves creating unique and valuable content for each product or page, using canonical tags to specify preferred versions of content, and avoiding unnecessary replication of information across your site.
Duplicate content and the Canonical Tag
The canonical tag is an HTML element that helps webmasters prevent duplicate content issues in SEO by specifying the “preferred” version of a web page. It’s a signal to search engines about which version of a page you consider to be the most important or authoritative. This way, even if there are multiple pages with similar content, search engines know which one to prioritise in search results, helping to avoid dilution in rankings.
Example of the canonical in action
Suppose you have two URLs with similar content:
<http://www.example.com/product><http://example.com/product?color=blue&size=medium>
To indicate that the first URL is the preferred one (the canonical version), you would add the following tag in the <head> section of the HTML of the second URL’s page:
<link rel="canonical" href="<http://www.example.com/product>" />Tips for proper implementation
- Specify one Canonical URL per content piece: For each piece of content on your site, choose one URL as the canonical version. This should be the version you want users to see and the one you consider to be the most authoritative.
- Use absolute URLs: Always specify the absolute path in the
hrefattribute of the canonical tag (i.e., the full URL including<http://> or<https://).> This removes any ambiguity for search engines. - Apply tags consistently: Ensure the canonical tag is used consistently across your site. Inconsistent use can confuse search engines and potentially dilute your SEO efforts.
- Include in all versions: Place the canonical tag in the
<head>section of the HTML of all versions of the page, not just on the duplicate pages. This reinforces the signal to search engines about which page is canonical. - Verify with webmaster tools: Use tools like Google Search Console to check that your canonical tags are recognised and correctly interpreted by search engines. This can help you catch and correct any issues with your implementation.
By properly using the canonical tag, you can help search engines understand your site’s content structure better, prevent SEO problems related to duplicate content, and ensure that your pages are ranked as effectively as possible.
Topic clusters
Topic clusters are a way to organise your website’s content by focusing on main themes, which helps both people visiting your site and search engines find what they’re looking for more easily.
In this setup, you have a main “pillar” page that covers a broad topic in detail. Then, you create smaller “cluster” pages that talk about specific parts of that big topic. This makes it easier for visitors to find all the information they need on a subject and helps search engines see how your content links together. By showing search engines that your site has lots of good information on a particular subject, your site can become more of an authority and rank higher.
Content clusters: a practical example
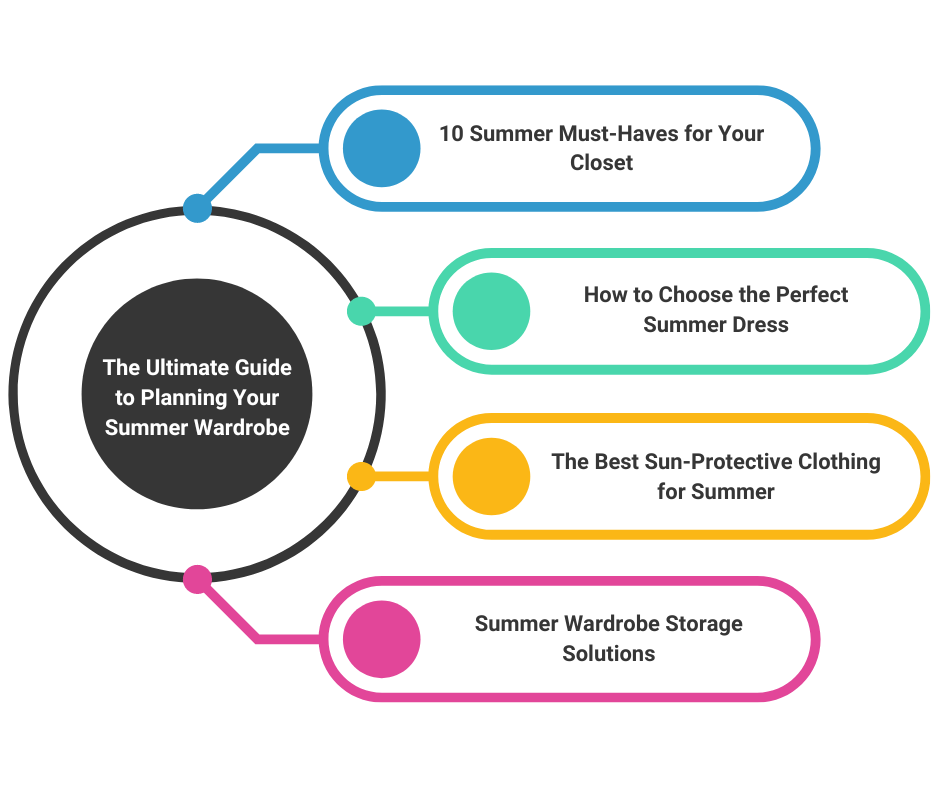

For an eCommerce site focusing on fashion, a topic cluster on “summer wardrobe planning” could be implemented as follows:
- Pillar page: This could be a comprehensive guide titled “The Ultimate Guide to Planning Your Summer Wardrobe”, covering everything from the essentials of a summer wardrobe to maintenance tips for summer clothes. This page links out to all the cluster content, providing a gateway for deeper exploration.
- Cluster pages: Each cluster page would explore a subtopic in detail. Examples include:
- “10 Summer Must-Haves for Your Closet”: Focusing on essential items for a summer wardrobe.
- “How to Choose the Perfect Summer Dress”: Offering advice on selecting dresses based on body type, occasion, and material.
- “The Best Sun-Protective Clothing for Summer”: Highlighting clothing options that offer UV protection.
- “Summer Wardrobe Storage Solutions”: Tips for storing winter clothes and keeping summer clothes in perfect condition.
By linking these cluster pages back to the pillar page, you signal to search engines that the pillar page holds comprehensive authority on the topic. This not only enhances the user journey by providing them with a structured way to navigate through your content but also improves SEO by highlighting your site’s expertise and relevance in the field of summer fashion.
This method of organising content around topic clusters establishes your site as a go-to resource for summer wardrobe planning, while aligning with SEO best practices, enhancing your visibility in search engine results.
Boost your traffic and sales with our essential eCommerce SEO audit checklist
Wrapping up, if you want to boost your online shop’s visibility, get more visitors, and see your sales climb, going through an SEO audit is the way to go.
By paying attention to the key areas we’ve talked about—like making sure your website is easy for search engines to read, building strong links from other sites, making your website fast and user-friendly, and creating content that speaks directly to your customers—you’re laying down the groundwork for success.
SEO isn’t just a one-off job; it’s an ongoing journey. Staying updated with the latest in SEO and continually refining your strategy will keep you ahead of the game.
By following the steps in our checklist, you’re not just boosting your site’s ranking but also making sure people enjoy using your site, which means they’re more likely to stick around, buy, and even come back for more.
Need a helping hand? As an eCommerce agency with skills in eCommerce SEO, we’re here to help you get more organic traffic and sales.
Here’s how we can help:
- Personalised SEO audits: Tailored assessments to identify specific areas for improvement on your website.
- Actionable insights: Detailed reports with clear, actionable steps to boost your site’s performance.
- Ongoing support: Continuous monitoring and support to ensure your SEO strategy stays effective.
- Expert guidance: Access to our team of SEO professionals.
Don’t let SEO challenges hold you back.
